Why You Should Add Stinging Nettle to Your Diet

According to Healthline, Urtica dioica comes from the Latin word ‘uro,’ which means “to burn,” because stinging nettle can cause a temporary burning sensation upon contact. The stems and leaves of stinging nettle are covered with needle-like hairs, called trichomes. Each trichome contains a mix of irritating compounds, including histamine, acetylcholine, serotonin, and formic acid (via Brooklyn Botanical Garden). The little hairs are brittle, and they break off and cling to hair and skin, which can cause irritation, itching, redness, and swelling. But there’s no need to withstand a rash to reap the benefits of stinging nettle; once it’s been dried, freeze-dried, or cooked, it’s safe to consume (via Healthline). This plant has been used for centuries; Ancient Egyptians used stinging nettle to treat arthritis and lower back pain, and Roman troops rubbed it on themselves to keep warm.
Stinging Nettle Makes a Great Dietary Supplement
Because stinging nettle contains ingredients that regulate blood sugar, decrease inflammation, and increase urination, it’s used to treat diabetes, osteoarthritis, urinary tract infections, kidney stones, and muscle pain. When consumed as an extract, stinging nettle has been shown to improve blood sugar metabolism in mice (via MSN). When consumed as an herb (as opposed to the extract), stinging nettle seems to affect our metabolism and the way we burn fat positively. A recent study by the University of Maryland revealed that feeding mice the leaves from the stinging nettle plant prevented the critters from gaining weight — even while being fed a high-fat diet.

NC State Extension reports that topical creams containing stinging nettle are used for joint pain and various skin ailments, including eczema and dandruff. If you want to give stinging nettle a try, steep the dried leaves and flowers to make tea, or add the leaves, stems, and roots to soups, stews, smoothies, and stir-fries (via Healthline). Whether you try the extract, herb, or cream — remember this: The FDA doesn’t regulate the ingredients, strengths, and claims of herbal remedies or supplements, so always consult with your doctor first (via Medical News Today).

The Reason You Should Save Your Pasta Water isn’t Why You Think

A Sticker on a Butterfly’s Wings Travels More Than a Thousand Miles

Helping Your Cat Handle Holidays
Add Technological Flair to Your Kitchen With These New Devices

Cats May Recognize Their Own Names According to Science
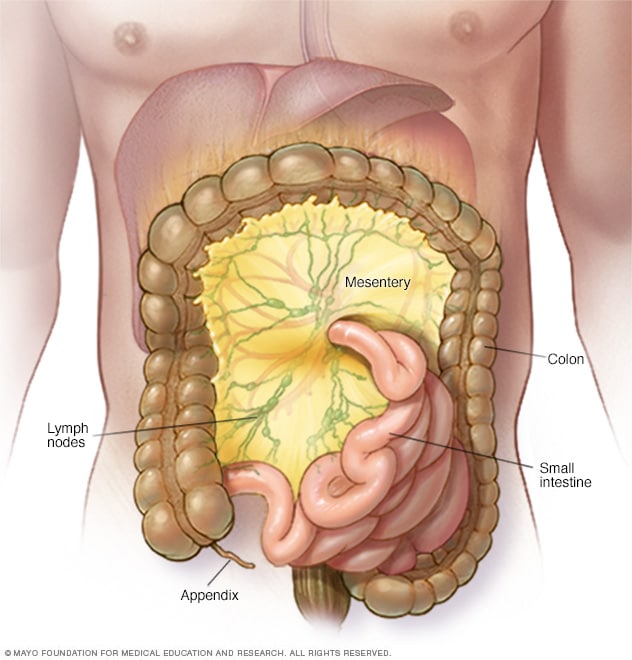
A New Organ Has Officially Been Discovered In The Human Body
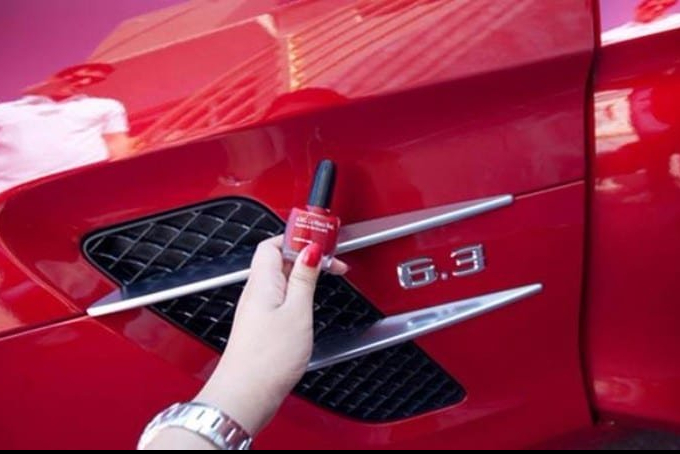

Secret Car Cleaning Hacks Revealed
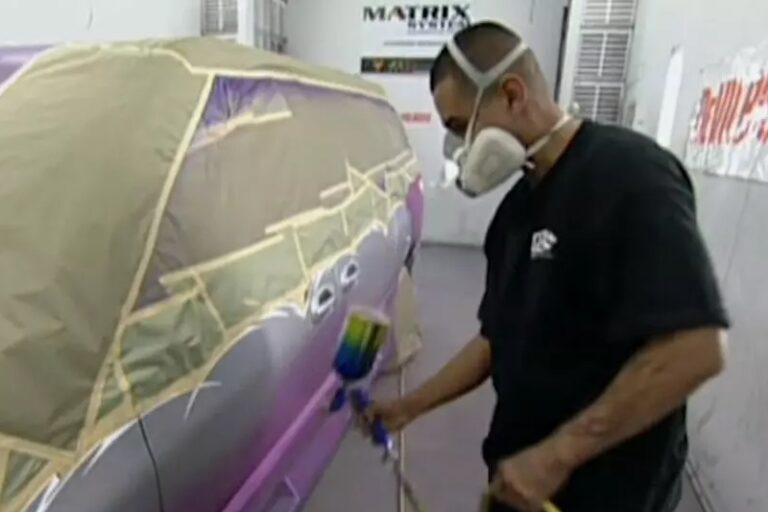

A Behind the Scenes Look at MTV’s Popular Show: Pimp My Ride
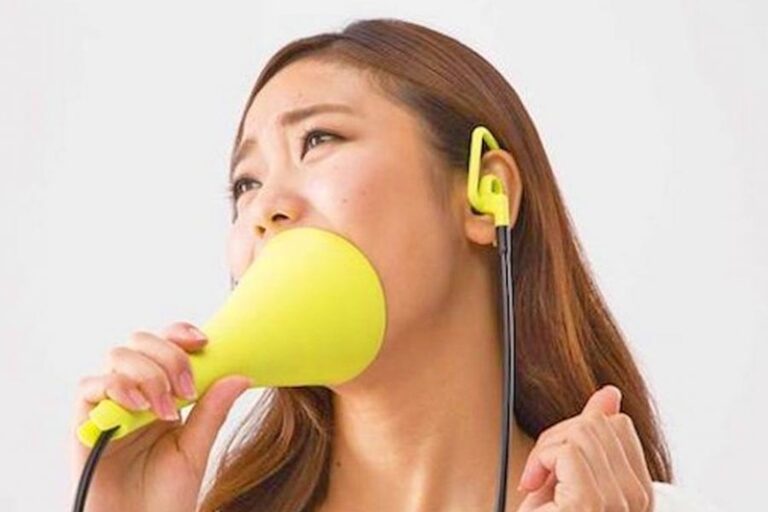

The Strangest Products From Amazon That People Actually Love
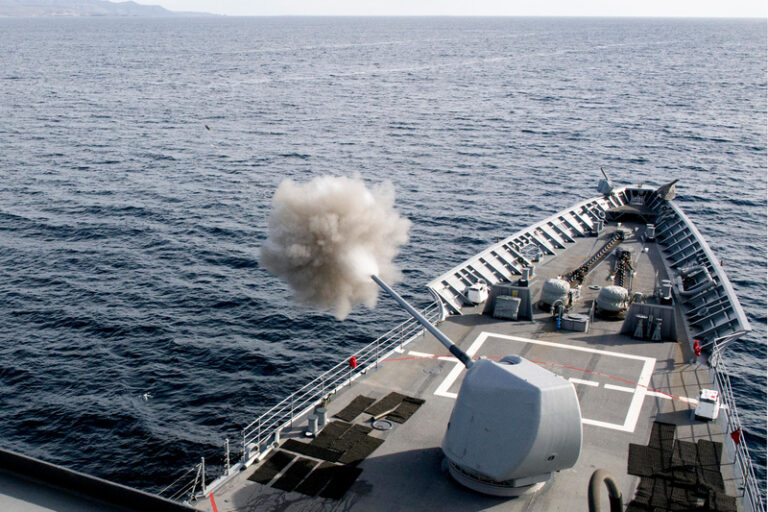

The Most Bizarre Weapons Used by U.S. Navy Units